CSP members’ contribution to the Strategic Plan for Biodiversity 2011-2020 and the Aichi Biodiversity Targets
The Consortium of Scientific Partners on Biodiversity (CSP) plays a central role on the successful implementation of the Strategic Plan for Biodiversity 2011-2020 and its Aichi Biodiversity Targets through capacity building and the promotion and offer of information, tools and services. For parties and other stakeholders to have a clear picture of how CSP can support them with CBD’s implementation, a questionnaire to map their contributions to the achievement of the Aichi Targets was distributed among them.
The questionnaire was responded by 15 of the 26 CSP members, who provided information on the actions they have undertaken since 2011, while specifying the level of contribution to each Aichi Target, and providing information to support each answer.
Click to enlarge 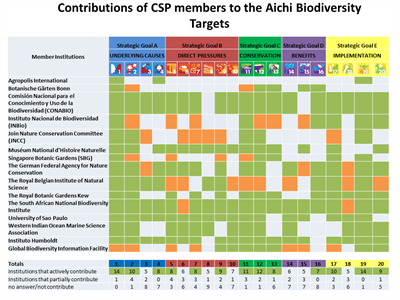
For details on each member’s contribution to the Aichi Biodiversity Targets, click the link to each specific institution.
Overview of the CSP members’ contributions to the Aichi Biodiversity Targets
Figure 1 shows the contributions of the CSP members who responded to the questionnaire, highlighting the Aichi Targets with the largest number of activities and projects addressing them. Target 1 (Awareness of Biodiversity), target 19 (Biodiversity Knowledge), target 12 (Preventing Extinctions), target 11 (Protected Areas) and target 2 (Integration of Biodiversity Values), registered the largest number of contributions from CSP members (blue dotted line). With the exception of target 12, these correspond with targets that -concerning GBO 4- have shown significant advances towards their accomplishment.
Click to enlarge 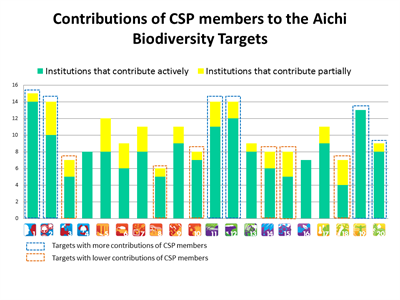
On the other hand, target 3 (Incentives), target 8 (Pollution), target 15 (Restoration and Resilience), target 18 (Traditional Knowledge), target 14 (Essential Ecosystem Services), and target 10 (Vulnerable Ecosystems), registered the smallest number of contributions from CSP members. Coincidently, most of these targets show no significant advances towards their accomplishment, while half of these (targets 8, 10 and 14) are even farther to their fulfillment than they used to in the recent past.
Click to enlarge 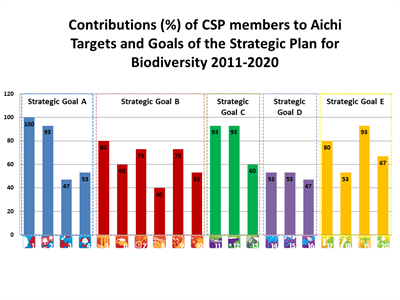
Figure 3 shows that most of the participant CSP members (more than 11) contribute to nine Aichi Targets, particularly those related to awareness of values of biodiversity and generation of scientific knowledge; conservation of protected natural areas and threatened species, as well as promoting sustainable productive practices. It also shows that Aichi target 8, related to environmental pollution, is the target with the least contributions from CSP members.
Click to enlarge 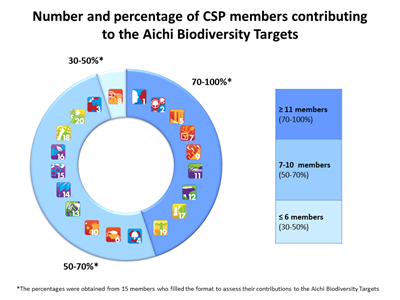
Concerning the five Strategic Goals that encompass the 20 Aichi Targets, Goal B, which addresses the underlying causes of biodiversity loss by mainstreaming biodiversity across government and society, received the largest amount of contributions from CSP members (28% of the total contributions),. On the other hand, Goal D, which seeks to enhance the benefits to all from biodiversity and ecosystem services, received the least contributions from CSP members (11 % of the total contributions),. However, it is important to mention that Goal D only has 3 targets while Goal B has 6 targets.
Click to enlarge 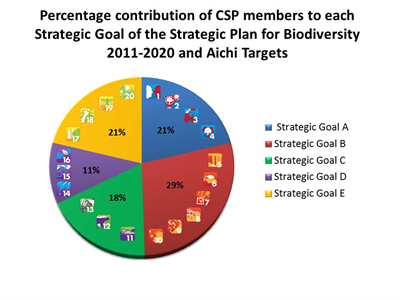 Back >
Back >